Table of Contents
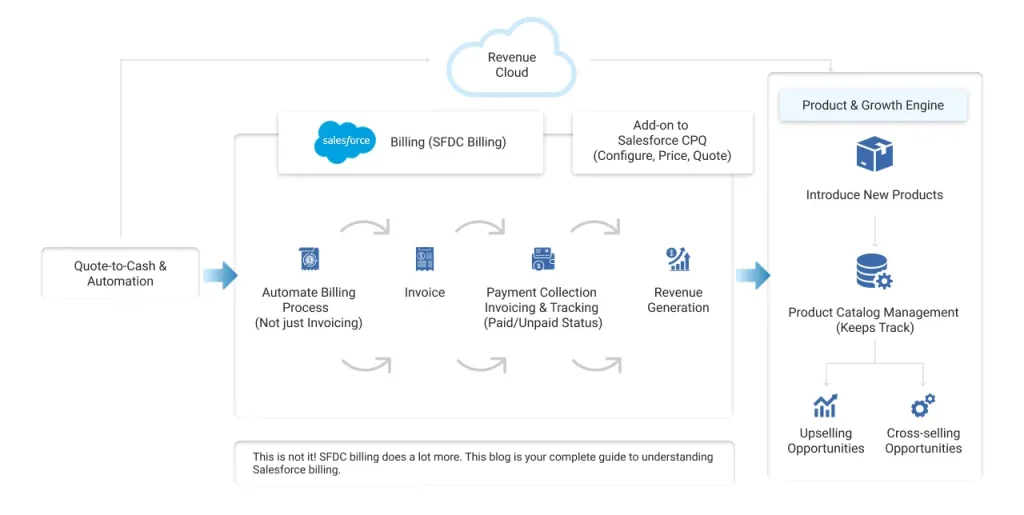
Salesforce Billing (SFDC billing) is a comprehensive billing solution within Salesforce, offered by Revenue Cloud. It is an add-on package to Salesforce CPQ (Configure, Price, and Quote) that helps businesses extend the quote-to-cash and automation capabilities within Salesforce. This is also known as Salesforce CPQ Billing.
Not limited to invoicing, billing in Salesforce extends beyond it by automating the entire billing process, from invoicing to payment collection and revenue generation. It automatically records all orders and tracks the payment against these orders, whether they are paid or not.
When you introduce new products in your business, Salesforce Billing can handle that efficiently by keeping track of everything you sell, namely your product catalog. This way, it helps you create the best opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
Let’s get started!
Types of Salesforce Billing

Here is a list of different Salesforce billing models and how they operate differently:
1. Subscription/recurring billing
Salesforce subscription billing, or recurring billing, involves charging customers repeatedly, be it monthly, quarterly, annually, or any set period. It automates renewals and proration (adjusting charges for mid-period changes) and helps in Salesforce invoicing.
This type of billing suits SaaS companies or any business offering ongoing services. For example, the New York Times, the best-selling newspaper, uses Salesforce to manage:
- digital news subscriptions,
- Analyzing subscriber behavior and
- personalizing offers.
2. Usage-based billing
Usage-based billing charges customers based on how much they use or consume a service or product. The billing amount varies by billing period, depending on how much the customer used the product or service.
For example, a cloud storage provider may bill customers monthly based on the amount of storage they use.
3. One-time billing
One-time billing is for single, non-recurring charges. Customers get billed once for a product or service, such as consulting fees, setup charges, or project completion fees. It can be invoiced independently or alongside recurring charges. Once the service is given or the product is purchased, this billing completes its cycle.
For example, a business consulting firm issues a one-time invoice when a project milestone is reached.
4. Deferred revenue billing
Deferred revenue billing refers to when the customer’s payment is postponed for a certain period after the product or service is delivered. It is like a grace period before the first payment is due. Deferred billing may sometimes include interest-free periods or promotional offers. While also ensuring compliance with accounting standards.
For example, a furniture store allows a customer to take a sofa home now but defers the payment for six months. The customer enjoys the product before making any payments.
5. Advance and arrears billing
In advance billing, as the name suggests, the invoices are generated and sent before the product or service is delivered.
In arrears billing, the customers are invoiced after the service period or after delivery is complete. This controls the invoice timing relative to service delivery.
For example, when you shop online, you prepay for a certain product or service before its delivery.
Key features of Salesforce Billing
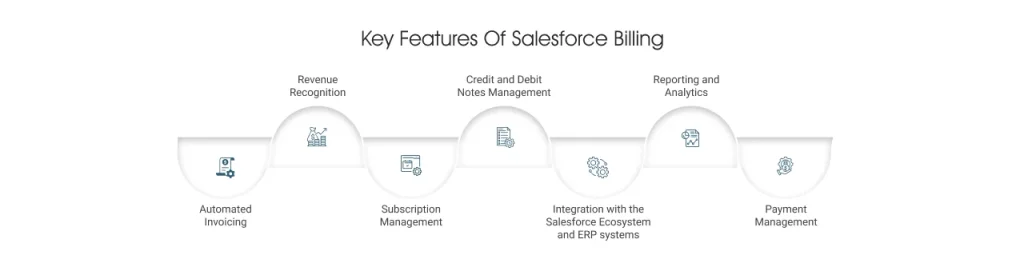
1. Automated invoicing
- SFDC billing automatically generates invoices as soon as a sales order or subscription is finalized.
- The order details are picked up and included in invoices. It includes details like products, quantities, prices, taxes, and discounts.
- Automates the lifecycle of the invoice from creation to customer delivery and tracking payment status.
2. Revenue recognition
- This feature helps businesses in recognizing and recording revenue while complying with accounting standards like ASC 606 and IFRS 15.
- It allows setting rules to recognize revenue over time (e.g., monthly for a yearly subscription) rather than all at once. By tracking recognition schedules, billing integrates those schedules into financial reporting.
3. Subscription management
- Salesforce subscription management supports the entire subscription lifecycle from creation, renewal, upgrades, downgrades, and termination.
- It handles proration of charges when subscription changes occur mid-cycle. Proration means charging customers only for the services they use within a billing cycle, rather than charging the full amount.
- You get automations for renewals and customer-side notifications related to subscription changes.
4. Credit and debit notes management
- Salesforce billing adjusts processes such as credit notes, debit notes, and refunds to keep customer billing accurate. It tracks and documents all adjustments within the system.
5. Integration with the Salesforce ecosystem and ERP systems
Being part of Salesforce CPQ, Billing ensures a smooth quote-to-cash process.
- It synchronizes billing data with ERP and financial systems for end-to-end business process management.
- API support allows customization and integration with third-party tools.
6. Reporting and analytics
- You can leverage customizable reports and dashboards to monitor billing performance, revenue trends, payment statuses, and subscription metrics.
- It provides real-time visibility into accounts receivable balances and financial health.
7. Payment management
- It manages customer payment information securely and integrates with payment gateways for credit card, ACH, and other payment methods.
- It tracks payment statuses to handle completed, unsettled, or skipped payments.
- It supports multiple ways to create payments. Be it through accounts receivable, admin scheduling, or customer self-service via a payment portal.
- Payments are matched to invoices and automatically applied to outstanding balances.
Here are the various critical aspects of ‘Payments’ in Salesforce billing:
- Payment Object: This is a financial object that stores a payment event, including details like the payment amount, payment type, and the account to which the payment could be applied.
- Payment Creation: It allows three different ways to create a payment:
- Through accounts receivable
- Through admins who can evaluate the posted invoices through scheduled payments
- Through end consumers. They can enter the Salesforce payment billing center and pay against invoices using their favorite payment methods.
- Payment Status: This checks the payment status of the invoices. Once they are completed, the funds are applied to one or more invoices.
- Payment Methods: This stores the customers’ ACH and credit card information and the payment gateways used for accepting payments.
- Processing Payments: This is responsible for gathering the customer’s payment information and passing it to their bank.
Benefits of Salesforce Billing
Here we have listed the business benefits that SFDC billing offers:
1. Faster and more accurate invoicing
Salesforce Billing eliminates manual data entry and reduces the risk of human error. This enables finance teams to move from order to invoice in Salesforce much faster, improving cash flow and billing accuracy.
2. Compliant and audit‑ready revenue reporting
The built‑in revenue recognition rules help organizations to stay aligned with standards like ASC 606 and IFRS 15. This leads to more reliable financial statements and easier audits, without relying on complex spreadsheets.
3. Streamlined subscription billing
It helps businesses in handling recurring revenue. With automated renewal workflows and real-time customer notifications, your teams spend less time on manual adjustments and more time on growth.
Unified quote‑to‑cash across systems
SFDC Billing ensures strong integration with Salesforce CPQ, CRM, ERP, and other financial tools that create a single source of truth for customer and billing data. It reduces data silos, minimizes reconciliation issues, and gives sales, finance, and operations teams a shared view of the revenue lifecycle.
4. Actionable financial insights
Real‑time reporting and analytics on billing, payments, and subscriptions enable better decision‑making for your business. You can quickly identify revenue trends and potential churn or cash‑flow risks earlier.
5. Stronger cash flow and lower leakage
Automation related to invoicing, payments, and collections reduces delays and missed transactions. Matching payments to invoices and tracking their statuses reduces revenue loss and boosts collections.
How does Salesforce Billing work?
Understand the working of Salesforce billing to customize steps as per your needs.
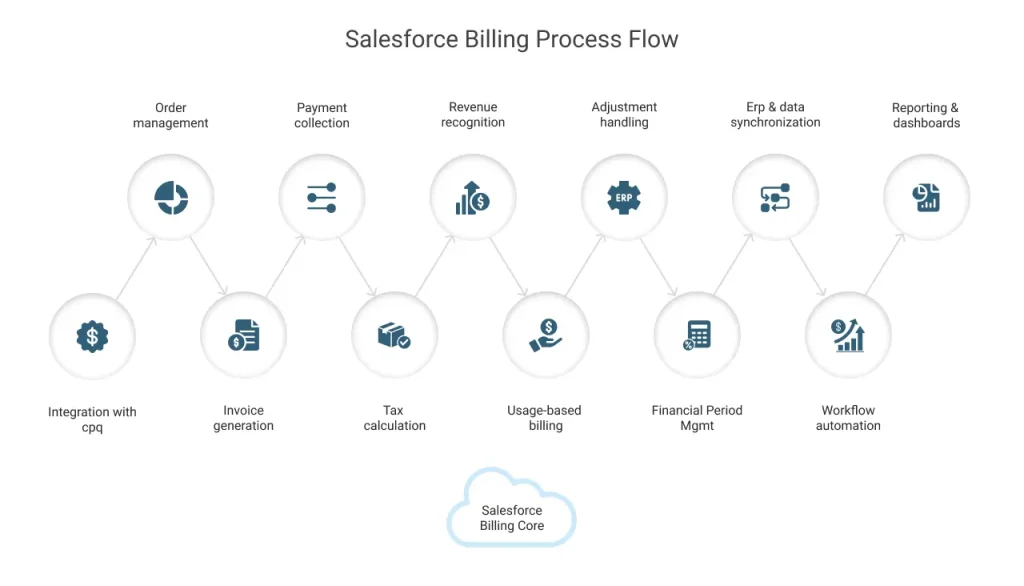
Step 1. Integration with Salesforce CPQ (Quote-to-Cash)
The process starts when a sales rep finalizes a quote in Salesforce CPQ. The key data from the quote, products, pricing, and terms are transferred to Salesforce Billing as an order record for further processing.
Step 2. Order management
The orders act as the bridge between CPQ and Billing.
Billing in Salesforce inherits details from the order object, including which products should be invoiced, different billing schedules, and their frequency. You can configure billing rules, charge types (recurring, usage-based, or one-time), billing frequency, and tax rules for each product and save the changes.
Step 3. Invoice generation
- Invoices are automatically generated based on the products serviced in the order and their billing type (one-time, recurring, or usage-based).
- Each invoice includes:
- purchased items/services,
- quantity,
- price,
- taxes,
- balance,
- and the due date.
- Billing schedules or product date fields determine the number and timing of invoices generated.
The “Bill Now” function lets you manually generate invoices for specific orders when required.
Step 4. Payment collection and allocation
After the invoice is generated, you know the amount of receivables. For the same, payments are to be posted manually or processed automatically via integrated payment gateways (credit card, ACH, etc.). Once it is done, the balance and payment status are updated in real time.
Step 5. Tax calculation
Taxes can be calculated using Salesforce Billing’s internal standard tax engine or integrated external tax services like Avalara and Vertex. Tax configuration involves setting tax rules and integrating with third-party tax services for accurate, automated tax reporting on invoices.
Step 6. Revenue recognition
After every calculation, the revenue schedules are generated for each invoice line. This helps recognize income over time or based on delivery milestones as per your business model. While you can automate compliance with accounting standards like ASC 606 and IFRS 15.
Step 7. Usage-based billing
Usage-based summaries are invoiced independently, allowing for flexible billing timeframes for usage products, such as in utilities and SaaS companies.
Step 8. Adjustment handling
Any adjustments are managed through credit and debit notes. Through this, you can handle refunds, additional charges, or corrections to customer accounts.
Step 9. Financial period management
Your finance teams must update the financial records and close the accounting periods, whether they are monthly or yearly. They should also ensure that the statements and ledgers are reconciled and current.
Step 10. ERP and data synchronization
Billing data is synchronized with ERP or financial systems for accounting, general ledger entries, and financial reporting, with mapping fields available for seamless integration.
Step 11. Workflow automation and customization
Automation features allow you to set trigger criteria for billing actions, invoice posting, reminders, and approvals, all reducing manual intervention.
Custom fields, Apex triggers, and automation rules can be defined for advanced business logic.
Step 12. Reporting and dashboards
The data and reports can be visualized in real-time on dashboards, offering visibility into billing performance, invoice statuses, and revenue recognition, supporting financial decision-making.
Note: This information is sourced from multiple Salesforce sources, such as its official documentation and Trailhead.
Salesforce Billing Best Practices
Here are a few best practices you must follow for a safe and successful implementation.

1. Implementing security measures
Ensure security to prevent unauthorized parties from accessing and misusing data for their own malicious purposes.
- Enable multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to user logins.
- Use strong passwords and frequently update them.
- Enable role-based access control so that users can access only the relevant information.
- Set up alerts for false patterns like multiple failed login attempts, which could indicate a security breach.
2. Providing training and support for users
Your business teams require training to get their hands on Salesforce Billing.
- Communicate clear training objectives to the users, including what they will learn, how they will learn, and how this learning will help them.
- Create a training plan and move forward accordingly. Minor changes could be entertained.
- Create a repository of training resources and materials you can refer to and share with the users.
- Incorporate learning into the user’s work routines and support them.
3. Keeping up with updates and enhancements
It is optimal to keep upgrading your Salesforce platform. Leverage the latest technologies and enhancements, as this introduces new features and enhanced capabilities into the existing features. Moreover, the latest security updates ensure protection from any new vulnerabilities and threats.
Keep on checking for updates and maintenance, and apply patches promptly.
4. Ensure regular audits
Conduct regular audits and checks of billing data, invoices, transactions, and revenue schedules to identify discrepancies and unauthorized transactions early.
5. Leverage automation tools
It is advised to use automation tools as much as you can. As it increases your productivity and saves time that might have gone into completing redundant tasks.
Use tools such as workflow rules, batch jobs, and scheduled processes to streamline recurring billing, payment runs, credit/debit notes, and invoice generation.
Now that we have learned about Salesforce billing and the benefits it offers, you might consider incorporating it into your business to experience seamless invoicing and billing. But billing is just one piece of the revenue cycle.
To maximize value and boost efficiency, businesses increasingly rely on payment processing and orchestration platforms that unify payment management, automate collection workflows, and connect multiple payment gateways in one secure, integrated solution.
While Salesforce Billing integrates with gateways, it has limitations like
- single gateway dependency,
- basic retry logic,
- and heavy PCI compliance overhead on businesses.
All these challenges can seamlessly be resolved by ChargeOn, a payment processing and orchestrating platform. It extends these capabilities by:
- Multi-Gateway Routing: Transactions are automatically routed to the best-performing or region-specific gateway.
- Smart Retry Logic: Failed payments are retried intelligently (time-of-day, method switching), reducing involuntary churn.
PCI Burden Offload: ChargeOn centralizes tokenization and compliance, lowering the risk and cost for IT teams.

How to set up Salesforce billing in your Salesforce instance?
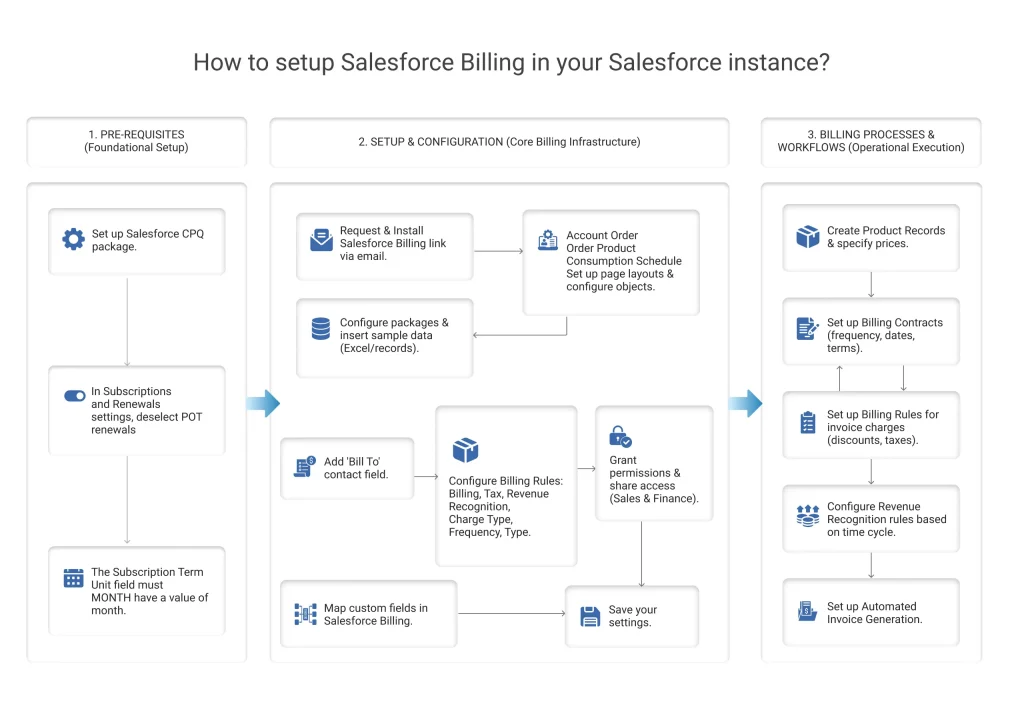
Pre-requisites
- Set up the Salesforce CPQ package.
- In Subscriptions and Renewals settings, deselect PoT renewals.
- The Subscription Term Unit field must have a value of month.
Let’s start with the setup
- Request a Salesforce Billing link to your registered email. Proceed with the same link further.
- Configure installed packages and insert sample data. This data can be your excel file or records.
- Set up your page layout and configure objects like account, order, order product, consumption schedule, and more.
- Add the bill to the contact field.
- Configure your products for Salesforce billing. Setup:
- Billing Rules
- Tax Rule
- Revenue Recognition Rules
- Charge Type
- Billing Frequency
- Billing Type
- Grant relevant permissions to your business teams. Focus on sharing access to sales and finance teams, primarily.
- Map custom fields in Salesforce billing with your objects.
- Save your settings.
Configure billing processes and workflows
- Start by creating various product records that you will offer to your customers. Then, specify the price against them. Use the structures defined in Salesforce billing.
- Set up billing contracts with details including the billing frequency, start and end dates, terms and conditions, and more.
- Set up billing rules that define how the charges would be applied to an invoice. Charges related to discounts, taxes, and more.
- Configure the revenue recognition rules based on your favorable time cycle.
- Set up automated invoice generation based on the rules and configurations above.
Salesforce Billing Pricing

Salesforce has not fixed a particular price for Salesforce billing. It might differ based on what services you are leveraging.
However, there are two different curated plans pre-made by Salesforce for your varying needs. Each of these versions has different features, and the cost upgrades as the version upgrades. Along with this, the cost also depends on how many users a business has.
Furthermore, the cost adds up if any add-on solution is engaged. Salesforce offers different levels of support and guidance for your business, which come at different costs. Therefore, for a clearer estimation, you can consult a Salesforce Consulting Partner. They understand all your requirements and suggest the best solution possible.
Final take
Billing in Salesforce is more than a back-office tool, as it can help businesses beyond automating Salesforce invoicing and accounting while streamlining the payment processes. It opens new possibilities for operational agility, improving customer experience and audit readiness.
The real opportunity lies in integrating Salesforce Billing with other advanced tools within your ecosystem, like customer portals, AI-driven analytics, or a flexible payment processing and orchestration platform like ChargeOn. When these tools work together, your quote-to-cash process not only becomes automated but also intelligent. It helps to forecast cash flow, respond to market changes, and reduce churn rate in real time.
The takeaway? Salesforce Billing is not just about billing; it is more about the development of a future-ready revenue engine for your business.













